Solutions Resources
If you’re designing and developing for the Internet of Things, you live in a low-throughput, low-power world.
Advances in video conference technologies let users collaborate across geographies, time zones, and even pandemics. But great experiences happen when every attendee feels immersed in the meeting, and their voices are heard.
Today, edge devices are everywhere, with tens of billions more expected to be deployed in the coming years.
What do on-demand language translation, self-driving cars, and video calls have in common? They’re all examples of today’s ubiquitous technology that was once the figment of science fiction (sci-fi).
For Linux developers who build low-level kernel and driver solutions, the open-source development model plays
We have conversations all the time with people trying to understand the business value of combining cloud computing and edge computing.
The international embedded computing community marked its 20th anniversary with this year’s Embedded World conference in Nuremberg.
The World Health Organization reports that over 50% of vaccines worldwide are wasted.
Today’s intelligent IoT edge devices can utilize cellular and Wi-Fi to connect with the cloud for reliable high-bandwidth and low-latency connectivity. But incorporating wireless connectivity into your IoT device is more involved than simply integrating a radio module.
There’s never a dull moment in the life of an embedded developer. They develop for different types of platforms with all sorts of software stacks, often on different OSs with vastly different architectures.
We're providing this update in case you missed our earlier blog post, or maybe just need a quick refresher.
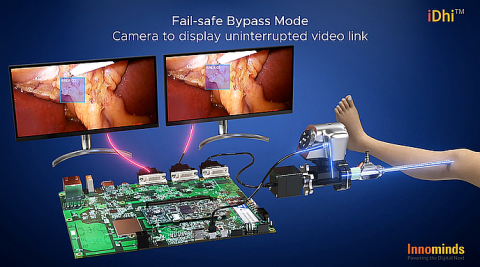
When it comes to real-time edge computing augmented by cloud backends, there is perhaps no better mission-critical use cases than those found in medical technology or MedTech.
As the world of IoT evolves, today’s uses cases and verticals demand that processing be done at or near the device edge.
Whether you’re a professional or hobbyist developer, you likely have some side-projects to help you discover new technology, learn how it works, or build solutions to hopefully make life easier.
Imagine yourself as a manager of an agricultural operation located where many would classify as – the middle of nowhere. Energy for some of your onsite services comes from large propane tanks, while fuel for your tractors is provided by tanker trucks that traverse the area.
Cities, agricultural lands, remote environments (e.g., streams), and buildings are all examples of environments where IoT technology is transforming them into smart connected spaces. The main aspect they share is the large geographical areas they span.
IoT and edge-cloud deployments can open up new possibilities to facilitate new business models and unlock societal benefits that serve the greater good.
Were you able to attend this year’s AWS re:Invent from November 29 – December 3?